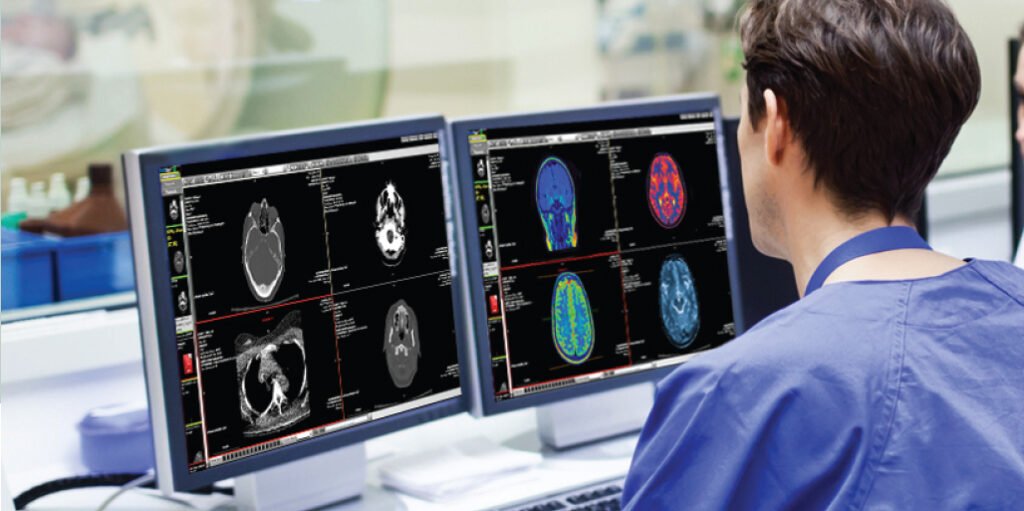
In the rapidly evolving world of healthcare, Picture Archiving and Communication Systems (PACS) have emerged as a cornerstone technology, revolutionizing how medical imaging is stored, accessed, and shared. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of PACS, its benefits, implementation, and future trends, providing an exhaustive resource for medical professionals and IT specialists alike.
What is a PACS System?
PACS (Picture Archiving and Communication System) is a medical imaging technology primarily used in healthcare organizations to securely store and digitally transmit electronic images and clinically relevant reports. The traditional method of storing images on physical films has been largely replaced by this digital solution, enabling quick and easy access to images from multiple modalities such as X-rays, CT scans, MRIs, and ultrasounds.
Key Components of PACS
- Image Acquisition Devices: These include X-ray machines, CT scanners, MRI machines, and ultrasound devices that capture medical images.
- Secure Network: Ensures the safe transmission of images and data across different systems and departments.
- Workstations: High-resolution monitors and computers that healthcare professionals use to view and analyze images.
- Archival Storage: Digital storage solutions, often cloud-based, that securely store medical images for long-term use.
Benefits of Implementing a PACS System
Enhanced Accessibility and Efficiency
PACS significantly enhances the accessibility of medical images. Instead of waiting for physical films to be developed and transported, images can be instantly accessed from any authorized workstation within the network. This immediate availability drastically improves the efficiency of patient care and streamlines workflows.
Improved Diagnostic Accuracy
High-resolution digital images can be manipulated (zoomed, adjusted for contrast, etc.), aiding in more accurate diagnoses. Radiologists and clinicians can compare current images with past records seamlessly, improving their ability to track disease progression or treatment effectiveness.
Cost-Effectiveness
Although the initial investment in PACS can be substantial, the long-term cost savings are significant. The reduction in the need for physical storage, film processing, and transportation leads to lower operational costs. Additionally, digital storage solutions are scalable, accommodating the growing volume of medical data without the need for extensive physical infrastructure.
Enhanced Collaboration and Sharing
PACS facilitates the easy sharing of medical images among healthcare professionals, regardless of their location. This feature is especially beneficial in telemedicine and for consultations between specialists in different geographical locations. The ability to share images in real time enhances collaborative efforts and improves patient outcomes.
Secure and Compliant Storage
PACS ensures that all medical images are stored securely, complying with regulatory standards such as HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act). This compliance is crucial for protecting patient privacy and maintaining the integrity of medical records.
Implementation Challenges and Solutions
High Initial Costs
The initial setup cost of a PACS system can be a barrier for some healthcare facilities. However, the long-term savings and improved operational efficiency often justify the investment. Additionally, various financing options and grants may be available to assist with the initial costs.
Integration with Existing Systems
Integrating PACS with other hospital information systems (HIS) and electronic medical records (EMR) can be challenging. It is essential to choose a PACS solution that offers robust interoperability and works seamlessly with existing systems. Comprehensive training for IT staff and end-users is also crucial to ensure a smooth transition.
Data Migration
Migrating existing medical images from physical films or legacy digital systems to a new PACS can be complex and time-consuming. Careful planning and execution are required to ensure data integrity and minimize disruptions during the transition period.
User Training
Adequate training for all users is essential for the successful implementation of PACS. This training should cover system navigation, image manipulation tools, and data security protocols to ensure that healthcare professionals can utilize the system effectively.
Future Trends in PACS
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) into PACS is set to revolutionize medical imaging further. AI algorithms can assist in image analysis, identifying anomalies that may be missed by the human eye, and providing diagnostic suggestions. This technology can significantly enhance diagnostic accuracy and speed.
Cloud-Based PACS
Cloud-based PACS solutions offer scalability, remote accessibility, and cost-effectiveness. They eliminate the need for extensive on-site hardware and provide a secure platform for storing and sharing medical images. As internet connectivity and cloud security continue to improve, more healthcare facilities are expected to adopt cloud-based PACS.
Mobile Access
The demand for mobile access to medical images is increasing. Future PACS solutions are likely to offer robust mobile applications, enabling healthcare professionals to access and share images from smartphones and tablets securely. This mobility can enhance the flexibility and responsiveness of medical services.
Interoperability Enhancements
Improving interoperability between PACS and other healthcare systems remains a priority. Enhanced interoperability ensures seamless data exchange, reducing redundancy and improving the overall efficiency of healthcare delivery.
FAQs about PACS Systems
What does PACS stand for in medical imaging?
PACS stands for Picture Archiving and Communication System. It is used to store, retrieve, manage, distribute, and present medical images electronically.
How does PACS improve patient care?
PACS improves patient care by providing quick and easy access to medical images, facilitating timely and accurate diagnoses. It also enables better collaboration among healthcare providers through easy sharing of images.
What are the main components of a PACS system?
The main components of a PACS system include image acquisition devices, a secure network, workstations for image viewing, and archival storage solutions.
Is PACS secure?
Yes, PACS systems are designed to be secure and comply with regulatory standards like HIPAA to protect patient data and ensure the integrity of medical records.
What are the benefits of a cloud-based PACS?
Cloud-based PACS offers scalability, cost savings, remote accessibility, and reduced need for on-site hardware. It also provides secure storage and easy sharing of medical images.
How does AI integration benefit PACS systems?
AI integration enhances PACS systems by assisting in image analysis, improving diagnostic accuracy, and speeding up the diagnostic process through advanced algorithms that can identify anomalies.